Substances such as marijuana, also known as “ganja,” are discussed quite a lot these days in the contemporary world. Since ganja is increasingly becoming legal and popular all over the globe, it becomes important to learn what it is, how it affects the body, and how it can be used both negatively and for healing purposes. As we cover this topic, we will also examine more closely how ganja impacts various systems of the body and the ill effects that may occur when it is used, particularly if it is done on a regular basis.
Ganja is essentially marijuana, a mind-altering substance extracted from the plant cannabis. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are the two most common of its numerous components. These drugs have instant and long-term impacts by connecting with the human body’s endocannabinoid system. There are individuals who consume ganja for entertainment reasons, but some use it medicinally, believing it would heal the symptoms of a specific illness. For any purpose, anyone considering taking ganja must be aware of the impact it has on the human body.
Ganja produces a variety of physical effects, and individuals will experience them differently based on their level of tolerance, dose, and method of use. Most of the time, ganja consumption produces short-term, psychoactive physical effects. Individuals can feel relaxed, euphoric, or have a distorted sense of time and space. Some individuals become more subdued, while others become more creative or sociable.
But ganja also has physical effects on the body as well as its psychological and emotional effects. One of the most universal and observable aftereffects is increased heart rate. This can cause extra stress to the cardiovascular system, which can be problematic for those with pre-existing heart conditions. Bloodshot eyes, parched lips (referred to as cotton mouth), and excessive hunger are also side effects of ganja known as the “munchies.”
The impacts of ganja also reach the lungs. A lot of the chemicals and carcinogens emitted by smoked marijuana are identical to those in tobacco, which can irritate the airways and may lead to respiratory issues in the long run.
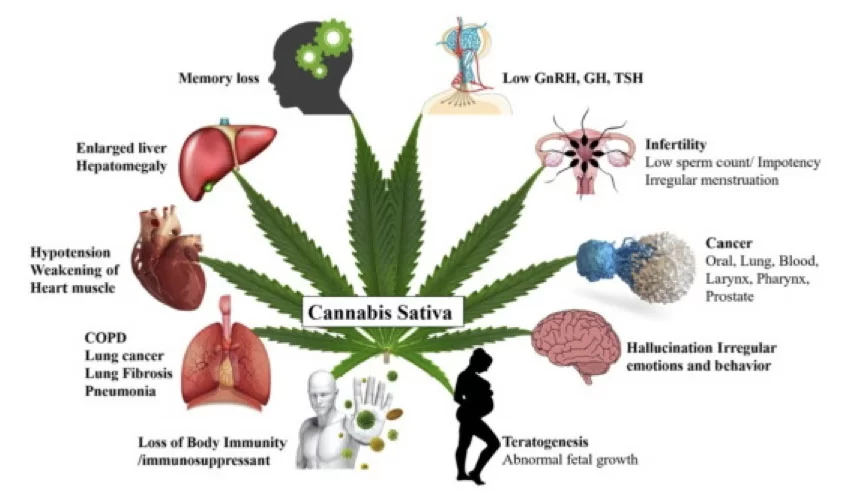
There are adverse effects on the body that cannot be overlooked, although ganja may have medicinal value and offer a fleeting high for those who derive relief. Several health problems can develop with heavy or regular use, some of which will not abate even after cessation.
The effect of ganja on brain function is one of its most troubling adverse effects. Repeated use can damage cognitive functions such as learning, memory, and attention. For adolescents whose brains are developing, this is especially troubling. Based on studies, frequent use of marijuana during adolescence has been found to reduce IQ and affect school performance, with long-term mental health consequences through adulthood.
In addition, the use of ganja can adversely affect mental well-being. Even though ganja can be used as a self-medication by some individuals to alleviate anxiety or depression, prolonged marijuana use has been found to induce or trigger mental illnesses. These include psychosis, paranoia, or anxiety in individuals who are susceptible to these conditions. It is advised that patients with pre-existing psychiatric illnesses use warnings when taking ganja since it can aggravate their condition or disturb treatment.
Risk of addiction is another harmful impact that should be noted. Ganja is likely to cause dependency even though it is not so physically addictive as alcohol or opioids. The normal user of ganja can develop psychological dependence and cannot function properly without it. This creates a pattern of using that influences all areas of their life, including their performance at work and in interpersonal relationships. While they are usually moderate in use, symptoms of withdrawal are anxiety, insomnia, and irritability.
Moreover, chronic ganja use could influence motivation and productivity. This effect, often termed “amotivational syndrome,” is when individuals become less interested in activities or goal-oriented behavior that previously pleased or satisfied them. In the context of academic or professional performance, where dedication and motivation are necessary to be successful, this influence may be especially worrisome.
There are also long-term risks of ganja consumption beyond the immediate ones. As noted previously, ganja smoking can cause harm to the lungs. From inhaling smoke, chronic use of marijuana has been associated with bronchitis and other lung problems. Though more studies need to be done to fully determine the long-term effects, there is also the worry of increased cancer risk.
Psychologically, the long-term use of ganja has been found to increase one’s risk for schizophrenia and other disorders if he or she is prone to such. Since the developing brain could be more susceptible to the harmful effects of ganja, this is a concern, especially if one starts smoking it early on.
Additionally, it is not possible to downplay the effect ganja has on the hormonal system of the body. Long-term marijuana use has been associated with shifts in hormone levels, which have an effect on everything from the stress response to reproductive health, studies show. Long-term marijuana use among men has been associated with low levels of testosterone, which could influence sexual function as well as general health.
Overall, ganja is a multifaceted drug that influences the body positively and negatively. While it can bring immediate relief or gratification, the potential dangers of continued or frequent use should be considered. Decision-making regarding the use of ganja can be informed by what it is, how it works within the body, and what potential dangers it presents. Knowledge of the advantages and limitations of ganja enables individuals to apply it more responsibly and improve their decision-making for their overall health.