- Mumbai, New Delhi, Bangalore
- (+91) 81518 30000
- WhatsApp Now
- contact@vedawellnessworld.com
Welcome to a journey of healing and transformation at VEDA Luxury Rehabilitation and Wellness Centre, where we strive to understand and address addiction through a comprehensive, neurobiological lens. Our approach, tailored for individuals, combines luxury with flexibility, offering a unique blend of modern science and holistic therapies.
At the core of our philosophy is a deep exploration of neurobiological models of addiction, which highlight the intricate dance between the central nervous system and neurotransmitter pathways, particularly the dopamine pathway. We recognize addiction as a complex interplay of biology, learning processes, and individual differences.
The neurobiology of addiction is a fascinating exploration into the intricate workings of the human brain and its response to substances of abuse. The brain’s capacity to learn and adapt is a critical aspect of addiction, as repeated exposure to drugs of abuse induces changes in neural circuitry, leading to cravings and compulsive behaviour. Traditionally, addiction was seen through a pharmacological lens, focusing on tolerance-inducing drugs and their impact on the body. However, modern neurobiological models emphasize the role of learning in addiction, with a spotlight on the consequences of dysfunctional learning processes over time. As we dive deeper into the neurobiology of addiction, we unravel the intricacies of how substances hijack the brain’s natural reward system, shedding light on potential avenues for targeted interventions and comprehensive treatment approaches.
Central to neurobiological models is the concept of substances, such as heroin, cocaine, alcohol, and nicotine, activating pathways related to motivation and reward in the central nervous system. These substances share a commonality—they elicit the release of dopamine
in specific brain regions, driving the learning processes that associate these substances with pleasure and desirability.
Our bodies naturally release dopamine in response to rewarding stimuli, like sweet tastes indicating high-calorie foods. However, addictive substances hijack this system, causing an exaggerated release of dopamine. Over time, repeated use of these substances leads to permanent or semi-permanent changes in the brain, creating a strong, disproportionate influence over behaviour.
While neurobiological models initially seem aligned with biomedical disease conceptions, they offer a crucial insight—learning processes play a central role. This insight opens the door for behavioural interventions designed to reverse these learning processes, presenting a unique opportunity for psychologists to contribute significantly.
Addiction involves complex interactions within the brain, implicating specific areas and neurotransmitter pathways. Here are some key brain areas and pathways implicated in addiction
Located in the midbrain, the VTA is a crucial component of the brain’s reward system. It plays a pivotal role in the release of dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reinforcement.
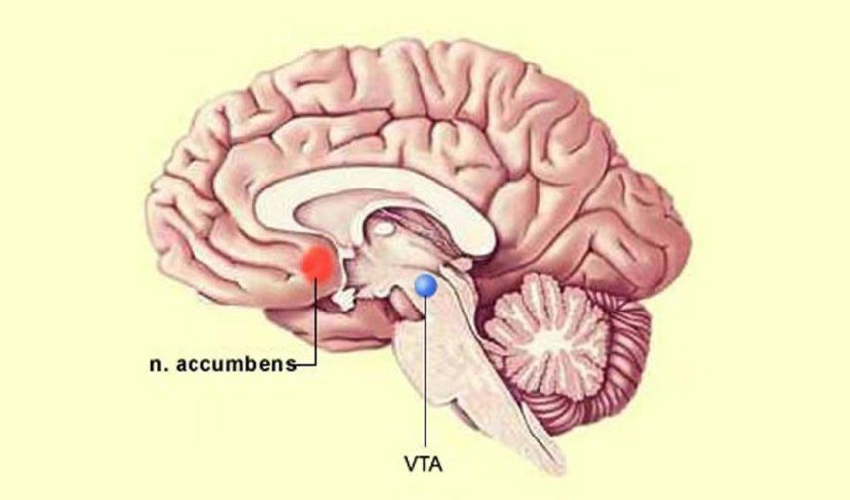
Often referred to as the brain’s “pleasure centre,” the NAc is a key component of the reward pathway. It receives signals from the VTA and is heavily involved in the reinforcing effects of addictive substances.
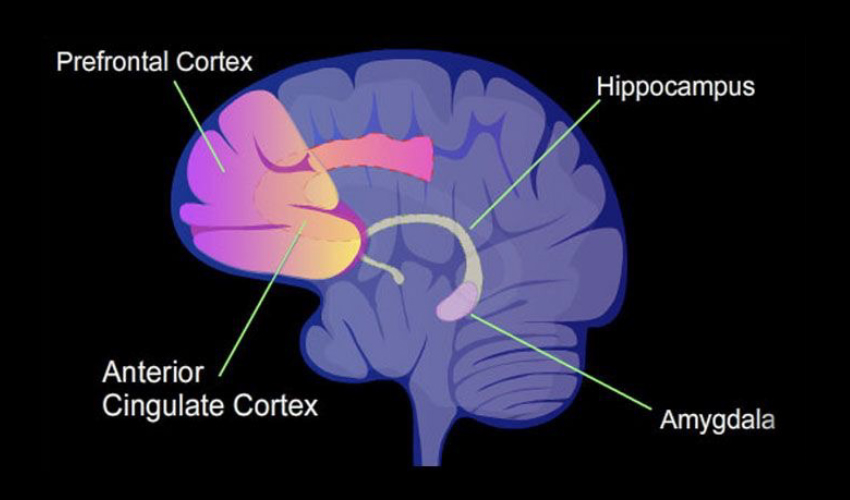
The PFC, particularly the prefrontal cortex, is responsible for executive functions such as decision-making, impulse control, and judgment. Dysfunction in this area is associated with the loss of control seen in addiction.
The amygdala is involved in the processing of emotions, including pleasure and stress. It plays a role in forming associations between drug-related cues and the rewarding effects of substances, contributing to cravings.
Critical for learning and memory, the hippocampus is involved in forming associations between drug-related cues and the context in which drug use occurs. This contributes to the persistence of drug-seeking behaviour.
The basal ganglia, including the striatum, is implicated in habit formation and motor functions. In addition, this area plays a role in the development of automatic, compulsive drug-seeking behaviours.
Glutamate is an excitatory neurotransmitter involved in learning and memory. Altered glutamate transmission is observed in addiction, influencing synaptic plasticity and contributing to the reinforcing effects of drugs.
The brain’s endogenous opioid system, including receptors like mu, delta, and kappa receptors, plays a role in modulating the rewarding effects of drugs. Opioid receptors are the target of drugs like heroin and prescription opioids.
This system, involving receptors like CB1, interacts with cannabinoids, affecting reward, motivation, and learning. Cannabis and synthetic cannabinoids influence this system.
While often associated with mood regulation, serotonin is also involved in the regulation of impulse control and decision-making. Dysfunction in the serotonin system is implicated in some addictive behaviour.
At VEDA, we recognize the importance of individuals monitoring and developing strategies to navigate high-risk situations, empowering them to take control of their recovery journey.
At VEDA Luxury Rehabilitation and Wellness Center, our approach to addiction treatment is centred around a comprehensive and personalized strategy, acknowledging the intricate neurobiology involved in addictive behaviours. Here’s a snapshot of the key aspects we focus on:
We employ MAT to alleviate withdrawal symptoms, reduce cravings, and normalize brain function. Our experienced medical team utilizes medications like methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone tailored to address the specific needs of individuals struggling with opioid or alcohol addiction.
VEDA emphasizes various therapeutic approaches, including Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Contingency Management, to modify learned behaviours associated with addiction. These interventions empower individuals to identify and change negative thought patterns, reinforcing positive behaviours and promoting abstinence.
Our commitment to fostering awareness and understanding is evident in our psychoeducational programs. We educate individuals about the neurobiological aspects of addiction, empowering them with the knowledge to make informed choices and actively engage in their recovery journey.
Techniques such as mindfulness meditation are incorporated into our programs to help individuals manage stress, cravings, and impulsive behaviours. Mindfulness practices have shown efficacy in promoting emotional regulation and reducing the risk of relapse.
Recognizing the importance of familial support, VEDA actively engages family members in the treatment process. Our family therapy sessions address dynamics, and communication patterns, and provide essential support to contribute significantly to an individual’s recovery.
Regular physical activity is integrated into our treatment plans, positively impacting brain function and mood. Exercise at VEDA contributes to the restoration of neural pathways affected by addiction and enhances overall well-being.
Our holistic approach includes a focus on a balanced and healthy diet to support overall brain health. Nutritional counselling and supplementation address deficiencies, fostering the recovery process.
We integrate holistic practices like yoga, acupuncture, and art therapy into our treatment plans, recognizing the importance of the mind-body connection. These practices provide additional tools for coping with stress and cravings.
VEDA prioritizes the development of comprehensive aftercare plans for sustained recovery. Ongoing therapy, support groups, and periodic check-ins are integral components to monitor progress and address emerging challenges.
By combining these targeted interventions, VEDA ensures individuals receive a well-rounded, personalized approach to addiction treatment that addresses both the biological and psychological components of the neurobiology of addiction. Our ultimate goal is to guide individuals not only towards achieving abstinence but also in building a fulfilling and sustainable life in recovery.
Contact us on 081518 30000 today and take the first step toward a brighter, addiction-free future.
